Flow Gaussian Mixture Model (FlowGMM)
This repository contains a PyTorch implementation of the Flow Gaussian Mixture Model (FlowGMM) model from our paper
Semi-Supervised Learning with Normalizing Flows
by Pavel Izmailov, Polina Kirichenko, Marc Finzi and Andrew Gordon Wilson.
Introduction
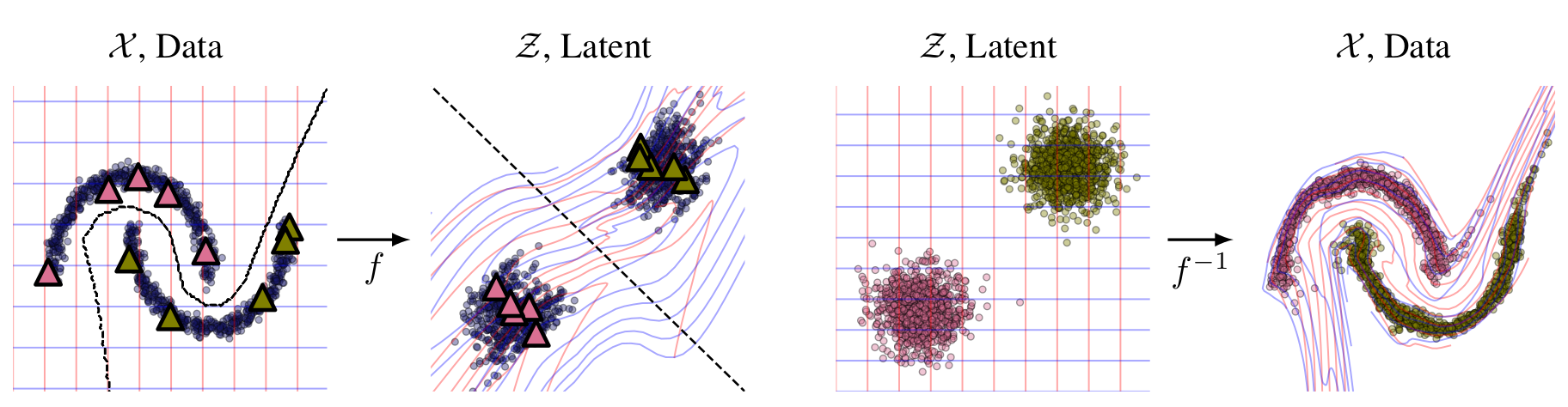
Normalizing flows transform a latent distribution through an invertible neural network for a flexible and pleasingly simple approach to generative modelling, while preserving an exact likelihood. In this paper, we introduce FlowGMM (Flow Gaussian Mixture Model), an approach to semi-supervised learning with normalizing flows, by modelling the density in the latent space as a Gaussian mixture, with each mixture component corresponding to a class represented in the labelled data. FlowGMM is distinct in its simplicity, unified treatment of labelled and unlabelled data with an exact likelihood, interpretability, and broad applicability beyond image data.
We show promising results on a wide range of semi-supervised classification problems, including AG-News and Yahoo Answers text data, UCI tabular data, and image datasets (MNIST, CIFAR-10 and SVHN).
Please cite our work if you find it useful:
@article{izmailov2019semi,
title={Semi-Supervised Learning with Normalizing Flows},
author={Izmailov, Pavel and Kirichenko, Polina and Finzi, Marc and Wilson, Andrew Gordon},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1912.13025},
year={2019}
}
Installation
To run the scripts you will need to clone the repo and install it locally. You can use the commands below.
git clone https://github.com/izmailovpavel/flowgmm.git
cd flowgmm
pip install -e .
Dependencies
We have the following dependencies for FlowGMM that must be installed prior to install to FlowGMM
- Python 3.7+
- PyTorch version 1.0.1+
- torchvision version 0.2.1+
- tensorboardX
We provide the scripts and example commands to reproduce the experiments from the paper.
Synthetic Datasets
The experiments on synthetic data are implemented in this ipython notebook. We additionaly provide another ipython notebook applying FlowGMM to labeled data only.
Tabular Datasets
The tabular datasets will be download and preprocessed automatically the first time they are needed. Using the commands below you can reproduce the performance from the table.
| AGNEWS | YAHOO | HEPMASS | MINIBOONE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLP | 77.5 | 55.7 | 82.2 | 80.4 |
| Pi Model | 80.2 | 56.3 | 87.9 | 80.8 |
| FlowGMM | 82.1 | 57.9 | 88.5 | 81.9 |
Text Classification (Updated)
Train FlowGMM on AG-News (200 labeled examples):
python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --trainer_config "{'unlab_weight':.6}" --net_config "{'k':1024,'coupling_layers':7,'nperlayer':1}" --network RealNVPTabularWPrior --trainer SemiFlow --num_epochs 100 --dataset AG_News --lr 3e-4 --train 200
Train FlowGMM on YAHOO Answers (800 labeled examples):
python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --trainer_config "{'unlab_weight':.2}" --net_config "{'k':1024,'coupling_layers':7,'nperlayer':1}" --network RealNVPTabularWPrior --trainer SemiFlow --num_epochs 200 --dataset YAHOO --lr 3e-4 --train 800
UCI Data
Train FlowGMM on MINIBOONE (20 labeled examples):
python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --trainer_config "{'unlab_weight':3.}"\
--net_config "{'k':256,'coupling_layers':10,'nperlayer':1}" --network RealNVPTabularWPrior \
--trainer SemiFlow --num_epochs 300 --dataset MINIBOONE --lr 3e-4
Train FlowGMM on HEPMASS (20 labeled examples):
python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --trainer_config "{'unlab_weight':10}"\
--net_config "{'k':256,'coupling_layers':10,'nperlayer':1}" \
--network RealNVPTabularWPrior --trainer SemiFlow --num_epochs 15 --dataset HEPMASS
Note that for on the low dimensional tabular data the FlowGMM models are quite sensitive to initialization. You may want to run the script a couple of times in case the model does not recover from a bad init.
The training script for the UCI dataset will automatically download the relevant MINIBOONE or HEPMASS datasets and unpack them into ~/datasets/UCI/., but for reference they come from here and here. We follow the preprocessing (where sensible) from Masked Autoregressive Flow for Density Estimation.
Baselines
Training the 3 Layer NN + Dropout on
YAHOO Answers: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr=1e-3 --dataset YAHOO --num_epochs 1000 --train 800
AG-NEWS: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr 1e-4 --dataset AG_News --num_epochs 1000 --train 200
MINIBOONE: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr 1e-4 --dataset MINIBOONE --num_epochs 500
HEPMASS: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr 1e-4 --dataset HEPMASS --num_epochs 500
Training the Pi Model on
YAHOO Answers: python flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr=1e-3 --dataset YAHOO --num_epochs 300 --train 800 --trainer PiModel --trainer_config "{'cons_weight':.3}"
AG-NEWS: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr 1e-3 --dataset AG_News --num_epochs 100 --train 200 --trainer PiModel --trainer_config "{'cons_weight':30}"
MINIBOONE: python flowgmm_tabular_new.py --lr 3e-4 --dataset MINIBOONE --trainer PiModel --trainer_config "{'cons_weight':30}" --num_epochs 10
HEPMASS: python experiments/train_flows/flowgmm_tabular_new.py --trainer PiModel --num_epochs 10 --dataset MINIBOONE --trainer_config "{'cons_weight':3}" --lr 1e-4
The notebook here can be used to run the kNN, Logistic Regression, and Label Spreading baselines once the data has already been downloaded by the previous scripts or if it was downloaded manually.
Image Classification
To run experiments with FlowGMM on image classification problems you first need to download and prepare the data. To do so, run the following scripts:
./data/bin/prepare_cifar10.sh
./data/bin/prepare_mnist.sh
./data/bin/prepare_svhn.sh
To run FlowGMM, you can use the following script
python3 experiments/train_flows/train_semisup_cons.py \
--dataset=<DATASET> \
--data_path=<DATAPATH> \
--label_path=<LABELPATH> \
--logdir=<LOGDIR> \
--ckptdir=<CKPTDIR> \
--save_freq=<SAVEFREQ> \
--num_epochs=<EPOCHS> \
--label_weight=<LABELWEIGHT> \
--consistency_weight=<CONSISTENCYWEIGHT> \
--consistency_rampup=<CONSISTENCYRAMPUP> \
--lr=<LR> \
--eval_freq=<EVALFREQ> \
Parameters:
DATASET— dataset name [MNIST/CIFAR10/SVHN]DATAPATH— path to the directory containing data; if you used the data preparation scripts, you can use e.g.data/images/mnistasDATAPATHLABELPATH— path to the label split generated by the data preparation scripts; this can be e.g.data/labels/mnist/1000_balanced_labels/10.npzordata/labels/cifar10/1000_balanced_labels/10.txt.LOGDIR— directory where tensorboard logs will be storedCKPTDIR— directory where checkpoints will be storedSAVEFREQ— frequency of saving checkpoints in epochsEPOCHS— number of training epochs (passes through labeled data)LABELWEIGHT— weight of cross-entropy loss term (default:1.)CONSISTENCYWEIGHT— weight of consistency loss term (default:1.)CONSISTENCYRAMPUP— length of consistency ramp-up period in epochs (default:1); consistency weight is linearly increasing from0.toCONSISTENCYWEIGHTin the firstCONSISTENCYRAMPUPepochs of trainingLR— learning rate (default:1e-3)EVALFREQ— number of epochs between evaluation (default:1)
Examples:
# MNIST, 100 labeled datapoints
python3 experiments/train_flows/train_semisup_cons.py --dataset=MNIST --data_path=data/images/mnist/ \
--label_path=data/labels/mnist/100_balanced_labels/10.npz --logdir=<LOGDIR> --ckptdir=<CKPTDIR> \
--save_freq=5000 --num_epochs=30001 --label_weight=3 --consistency_weight=1. --consistency_rampup=1000 \
--lr=1e-5 --eval_freq=100
# CIFAR-10, 4000 labeled datapoints
python3 experiments/train_flows/train_semisup_cons.py --dataset=CIFAR10 --data_path=data/images/cifar/cifar10/by-image/ \
--label_path=data/labels/cifar10/4000_balanced_labels/10.txt --logdir=<LOGDIR> --ckptdir=<CKPTDIR> \
--save_freq=500 --num_epochs=1501 --label_weight=3 --consistency_weight=1. --consistency_rampup=100 \
--lr=1e-4 --eval_freq=50
References
- RealNVP: github.com/chrischute/real-nvp